- Home
- Speciality
- Neonatology
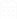
Care for Your Newborn
Our neonatology unit provides specialized care for newborns, especially premature babies or those with health complications

Services Offered
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU LEVEL III)
Advanced care for premature, low-birthweight, and critically ill newborns.

Preterm Baby Care
Specialized monitoring and nutrition management for premature infants.

Ventilator Support
Mechanical ventilation and CPAP for respiratory distress and premature lung development.

Phototherapy
Treatment for neonatal jaundice using advanced phototherapy systems.

Neonatal Resuscitation
Immediate stabilization and resuscitation of newborns in delivery rooms.

Infection Control
Strict protocols to prevent neonatal infections and sepsis.

Congenital Anomaly Management
Diagnosis, stabilization, and coordination for surgical correction of birth defects.

Nutritional Support
Customized feeding plans, including parenteral and enteral nutrition.

Neonatal Screening Programs
Metabolic, genetic, and hearing screening for early detection of disorders.

Therapeutic Hypothermia
Treatment for birth asphyxia to prevent brain injury.

Transport Services
Neonatal transport facilities for critically ill babies requiring advanced care.

Immunization Programs
Vaccination services to protect newborns against preventable diseases.
Services Offered
Advanced care for premature, low-birthweight, and critically ill newborns.
Specialized monitoring and nutrition management for premature infants.
Mechanical ventilation and CPAP for respiratory distress and premature lung development.
Treatment for neonatal jaundice using advanced phototherapy systems.
Immediate stabilization and resuscitation of newborns in delivery rooms.
Strict protocols to prevent neonatal infections and sepsis.
Diagnosis, stabilization, and coordination for surgical correction of birth defects.
Customized feeding plans, including parenteral and enteral nutrition.
Metabolic, genetic, and hearing screening for early detection of disorders.
Treatment for birth asphyxia to prevent brain injury.
Neonatal transport facilities for critically ill babies requiring advanced care.
Vaccination services to protect newborns against preventable diseases.
Advanced Care and Equipment's
Phototherapy
Neonatal phototherapy is a treatment for newborn jaundice that uses a special type of light to help a baby’s liver break down and remove bilirubin from their blood.
Ventilation HFO
These are designed for infants and have features like dedicated neonatal ventilation modes, automatic leakage compensation, and pressure and volume control
Point of care ultrasonography
(POCUS)
Point-of-care ultrasonography is a non-ionizing imaging technique that involves a clinician performing and interpreting ultrasound scans.
Baby warmer
Warmers, in general, are used to heat fluids before injection to prevent hypothermia following a surgical procedure. Similarly, blankets are warmed before use in a blanket warmer to reduce the patient’s heat loss.
Phototherapy
Ventilation HFO
Point of care ultrasonography (POCUS)
Baby warmer


Meet Our team of Specialists
Meet Our team of Neonatologist






Downloadable Resources
Common Newborn Conditions: Information about conditions like tongue-tie, reflux, and diaper rash.

Immunizations: Importance, schedule, and potential side effects.

Newborn Care Basics: Diapering, bathing, feeding, and soothing.

Support Group Information: Local support groups for new parents.

Downloadable Resources
Common Newborn Conditions: Information about conditions like tongue-tie, reflux, and diaper rash.

Immunizations: Importance, schedule, and potential side effects.

Newborn Care Basics: Diapering, bathing, feeding, and soothing.

Support Group Information: Local support groups for new parents.

Ask Our Experts: FAQs
Your baby will need a series of immunizations to protect them from various infectious diseases. The specific schedule will vary depending on your location and the recommendations of your pediatrician. However, some common childhood immunizations include:
- Diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DTP): Protects against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis.
- Polio: Protects against polio.
- Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR): Protects against measles, mumps, and rubella.
- Hib: Protects against Hemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) infection.
- Hepatitis B: Protects against hepatitis B infection.
- Varicella: Protects against chickenpox.
- Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV): Protects against pneumococcal infections.
- Rotavirus: Protects against rotavirus infection.
It’s important to follow the recommended immunization schedule and consult with your pediatrician for any questions or concerns.
Babies may need NICU care for various reasons, including:
- Premature birth
- Low birth weight
- Breathing problems (Respiratory distress syndrome, Meconium aspiration)
- Congenital abnormalities
- Jaundice
- Feeding problems
- Hypoglycaemia/ low blood sugar
- Infections
- Requirement for surgical intervention
- Difficult or complicated delivery
Yellowing of the skin and eyes indicates jaundice, caused by elevated bilirubin levels. Jaundice is common in newborns and usually appears 2-3 days after birth.
- Concerning signs include jaundice appearing in the first 24 hours or spreading to the legs.
- Severe jaundice can cause lethargy, poor feeding, or high-pitched crying.
Phototherapy is often used to treat significant jaundice. Regular follow-ups with your pediatrician can monitor bilirubin levels.
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) is the unexplained death of an infant. While the exact cause of SIDS is unknown, there are several steps you can take to reduce the risk:
- Put your baby to sleep on their back
- Share a room with your baby for the first six months
- Don’t smoke around your baby
- Breastfeed your baby, if possible
- Make sure your baby’s crib is safe and free of any loose bedding or pillows
It’s important to remember that while these steps can help to reduce the risk of SIDS, there is no guaranteed way to prevent it. If you have any concerns, talk to your pediatrician.